Task management, it’s not just about to-do lists; it’s about conquering your day, owning your goals, and actually achieving what you set out to do. This deep dive explores everything from choosing the right tools (Trello? Asana? A good old-fashioned notepad?) to mastering prioritization and collaboration. We’ll tackle procrastination head-on, explore how tech can help (or hinder!), and ultimately, help you become a productivity ninja.
We’ll cover different methodologies like Kanban and GTD, comparing their strengths and weaknesses. We’ll also delve into the importance of scheduling, prioritization techniques (like the Eisenhower Matrix), and how to build effective teams around shared tasks. Get ready to level up your organizational skills!
Defining Task Management
Task management is all about organizing and prioritizing tasks to improve efficiency and productivity. It’s not just about making to-do lists; it’s a strategic approach to tackling your workload, ensuring you’re focusing on the most important things first and getting stuff done. Think of it as the engine that drives your ability to achieve your goals.Effective task management relies on several core principles.
First, you need a clear understanding of your tasks – what needs to be done, by when, and why. Second, prioritization is key; not all tasks are created equal. Focusing on high-impact tasks first maximizes your output. Third, effective time management techniques help you allocate appropriate time slots for tasks, avoiding procrastination and burnout. Finally, consistent review and adjustment are crucial; your plan should be a living document that adapts to changing circumstances.
Task Management Methodologies
Several established methodologies offer structured approaches to task management. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses helps you choose the best fit for your needs. These methodologies provide frameworks for organizing, prioritizing, and completing tasks, ultimately improving productivity and reducing stress.
- Kanban: Kanban uses a visual board to represent the workflow. Tasks are represented as cards that move through columns representing different stages of completion (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done). This visual representation makes it easy to see the progress of tasks and identify bottlenecks. It’s highly adaptable and works well for managing individual tasks or team projects.
Imagine a whiteboard with sticky notes moving from one column to the next as work progresses.
- Scrum: Scrum is an agile framework commonly used in software development but applicable to other projects. It emphasizes iterative development, breaking down large projects into smaller, manageable sprints (typically 2-4 weeks). Each sprint has specific goals and a dedicated team working collaboratively. Daily stand-up meetings ensure everyone is aligned and potential roadblocks are identified quickly. Think of it as a highly structured, team-based approach to tackling complex projects.
- Getting Things Done (GTD): GTD is a personal productivity methodology focusing on capturing all tasks, clarifying next actions, organizing them, and then reflecting regularly on progress. It emphasizes capturing everything that needs to be done to clear your mind and allow for focused work on prioritized tasks. This system uses a multi-step process to ensure no task falls through the cracks, and involves regular review to ensure everything remains relevant.
Comparison of Task Management Approaches
The best task management approach depends heavily on individual preferences, the complexity of the tasks, and the number of people involved.
| Method | Best Suited For | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kanban | Visualizing workflow, individual or team projects, continuous improvement | Simple, visual, flexible, easily adaptable | Can become overwhelming with many tasks, less structured than other methods |
| Scrum | Complex projects, team collaboration, iterative development | Highly structured, promotes teamwork, regular feedback | Requires a dedicated team, can be overly complex for simple tasks |
| GTD | Personal productivity, managing many tasks, capturing everything | Comprehensive, clears mental clutter, promotes focus | Can be time-consuming to set up and maintain |
Tools and Technologies for Task Management

Okay, so you’ve got the hang of what task management
- is*, now let’s dive into the
- how*. Choosing the right tools is crucial for effective task management, and thankfully, there’s a whole universe of options out there, from super-simple to seriously sophisticated. We’ll look at a few popular choices and then weigh the pros and cons of going digital versus sticking with the old-school analog approach.
Popular Task Management Software
Picking the right software depends entirely on your needs and preferences. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, but some standouts consistently top the charts. We’ll compare three popular choices: Trello, Asana, and Todoist. Each offers a unique set of features, catering to different work styles and project complexities.
Comparison of Task Management Tools
The following table summarizes the key features, pricing, and ideal use cases for Trello, Asana, and Todoist. Remember that pricing models can change, so it’s always best to check the software’s website for the most up-to-date information.
| Name | Key Features | Pricing | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trello | Kanban boards, visual task organization, simple interface, integrations with other apps. | Free plan available; paid plans offer increased features and storage. | Project management for small teams, personal organization, simple workflow visualization. |
| Asana | Robust project management features, task dependencies, timelines, progress tracking, team collaboration tools. | Free plan available; paid plans unlock advanced features and support larger teams. | Complex projects, larger teams, detailed task management and collaboration. |
| Todoist | Intuitive task list management, prioritization features, subtasks, reminders, collaboration features. | Free plan available; paid plans offer additional features like collaboration and advanced filtering. | Personal task management, productivity enhancement, goal setting, simple project management. |
Digital vs. Analog Task Management
The age-old debate: digital or analog? Both have their strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right approach often depends on personal preference and the complexity of your tasks.
Advantages of Digital Task Management: Digital tools offer features like reminders, automated workflows, easy sharing and collaboration, and data backup. Imagine never missing a deadline again because of a smart reminder popping up on your phone! Or the ease of collaborating on a project with team members across different time zones.
Disadvantages of Digital Task Management: Over-reliance on technology can lead to distractions. Technical glitches and software updates can disrupt workflows. And some find the constant notifications overwhelming.
Advantages of Analog Task Management: The simplicity of pen and paper can be surprisingly effective. There’s no battery to die, no software crashes, and the tactile experience can improve focus for some. Many people find the act of physically writing things down helps them better remember and process information.
Disadvantages of Analog Task Management: Analog systems lack the automation and collaboration features of digital tools. Keeping track of everything can become cumbersome, especially for complex projects or large teams. And there’s always the risk of losing or misplacing your notes.
Task Prioritization and Scheduling
Effective task management isn’t just about listing tasks; it’s about strategically prioritizing and scheduling them to maximize productivity and meet deadlines. This involves understanding various prioritization techniques and effectively managing your time amidst inevitable interruptions.Prioritization methods help you focus on the most important tasks first, preventing you from getting bogged down in less critical activities. Proper scheduling ensures that tasks are allocated to specific time slots, enhancing your ability to track progress and maintain control over your workload.
Prioritization Techniques
Several proven methods exist for prioritizing tasks, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right method often depends on your personal preferences and the specific demands of the project. Two popular techniques are the Eisenhower Matrix and the MoSCoW method.The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Urgent-Important Matrix, categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance. Tasks are classified into four quadrants: Urgent and Important (Do First), Important but Not Urgent (Schedule), Urgent but Not Important (Delegate), and Neither Urgent nor Important (Eliminate).
This helps focus on high-impact activities while delegating or eliminating less crucial ones. For example, a looming deadline for a major project would fall into the “Do First” quadrant, while networking for future opportunities might be “Schedule.”The MoSCoW method prioritizes tasks based on their necessity: Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won’t have. “Must have” features are essential for the project’s success; “Should have” features are desirable but not critical; “Could have” features are less important and may be added later; and “Won’t have” features are excluded entirely.
Imagine developing a software application: core functionalities would be “Must have,” while advanced features might be “Should have” or “Could have,” depending on the project timeline and resources.
Sample Project Schedule
Let’s consider a hypothetical project: launching a new website. Using the Eisenhower Matrix, we can prioritize tasks and create a sample schedule.
| Task | Category (Eisenhower Matrix) | Deadline | Time Allocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design website layout | Important but Not Urgent | 2 weeks from now | 10 hours |
| Write website content | Important but Not Urgent | 1 week from now | 15 hours |
| Develop website functionality | Urgent and Important | 1 week from now | 25 hours |
| Test website functionality | Urgent and Important | 1 day before launch | 5 hours |
| Deploy website | Urgent and Important | Launch day | 2 hours |
This schedule prioritizes development and testing as urgent and important, allowing ample time for design and content creation before the launch deadline.
Managing Time Constraints and Interruptions
Even with a well-defined schedule, unexpected interruptions occur. To mitigate their impact:
- Time Blocking: Allocate specific time blocks for focused work on prioritized tasks, minimizing distractions.
- Buffer Time: Include buffer time in your schedule to accommodate unexpected delays or interruptions.
- Prioritization Re-evaluation: Regularly review your priorities and adjust your schedule as needed based on changing circumstances.
- Communication: Clearly communicate your schedule and availability to colleagues to minimize unnecessary interruptions.
For example, if an unexpected bug arises during website development, the buffer time allows for its resolution without jeopardizing the overall project timeline. Regular re-evaluation of priorities ensures that the most critical tasks always receive the necessary attention.
Teamwork and Collaboration in Task Management
Effective teamwork is the backbone of successful task management, especially in complex projects. Collaboration isn’t just about assigning tasks; it’s about fostering a shared understanding, clear communication, and mutual support to achieve common goals. This section will explore strategies for effective delegation and collaboration, illustrate a collaborative workflow, and address common challenges.
Successful task delegation hinges on clear communication and a well-defined process. It’s not just about assigning tasks, but also about providing the necessary context, resources, and support to ensure team members can complete their work effectively. Similarly, effective collaboration requires establishing clear communication channels, utilizing collaborative tools, and fostering a culture of trust and mutual respect.
Strategies for Effective Task Delegation and Collaboration
Effective task delegation requires careful consideration of individual team members’ skills and strengths. Matching tasks to abilities maximizes efficiency and minimizes frustration. Clear instructions, deadlines, and expected outcomes should accompany each delegated task. Regular check-ins and open communication channels ensure that everyone is on the same page and that any challenges are addressed promptly. Providing adequate support and resources, including access to necessary information and tools, is also crucial.
Finally, recognizing and appreciating individual contributions fosters a positive and collaborative work environment.
Collaborative Task Management Workflow Using Asana
Imagine a team using Asana to manage a marketing campaign launch. The workflow begins with a project creation in Asana, outlining the campaign’s overall goals and deadlines. The project manager then breaks down the campaign into smaller, manageable tasks (e.g., content creation, social media scheduling, email marketing). These tasks are assigned to individual team members based on their expertise.
Asana’s features, such as subtasks, due dates, and comments, facilitate task tracking and communication. Team members update their task statuses, add comments, and attach relevant files within Asana. The project manager monitors progress, provides support, and addresses any roadblocks. The visual representation of the workflow within Asana, including Gantt charts and progress bars, offers a clear overview of the campaign’s status and allows for proactive adjustments.
Finally, upon completion, the team reviews the campaign’s performance and documents lessons learned for future projects. This entire process is visible and transparent to all team members, promoting accountability and collaboration.
Challenges in Team Task Management and Proposed Solutions
Several challenges can hinder effective team task management. These challenges often stem from communication breakdowns, unclear roles and responsibilities, or a lack of appropriate tools and processes.
- Challenge: Communication breakdowns. Solution: Establish clear communication channels (e.g., regular team meetings, instant messaging, project management software) and ensure consistent updates.
- Challenge: Unclear roles and responsibilities. Solution: Create a detailed project plan outlining roles, responsibilities, and reporting structures. Use a RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) to clarify who is responsible for each task.
- Challenge: Lack of appropriate tools. Solution: Implement project management software (e.g., Asana, Trello, Monday.com) to facilitate task assignment, tracking, and collaboration.
- Challenge: Lack of accountability. Solution: Establish clear deadlines and expectations, and regularly monitor progress. Use performance metrics to track individual and team performance.
- Challenge: Conflicting priorities. Solution: Implement a prioritization system (e.g., MoSCoW method) to ensure that the most important tasks are addressed first. Regularly review priorities to adapt to changing circumstances.
Measuring Task Management Effectiveness
So, you’ve got your task management system up and running. But how do you know if it’s actuallyworking*? Measuring effectiveness isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about understanding if your system is helping you achieve your goals more efficiently and effectively. This involves tracking key metrics and using that data to make improvements.Effective task management hinges on quantifiable results.
Without data, improvements are guesswork. By tracking specific metrics, you can identify bottlenecks, celebrate successes, and ultimately, optimize your workflow for peak productivity. This section will Artikel key metrics and provide practical examples of how to leverage data for continuous improvement.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Task Management System Success
Several key metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of your task management system. These metrics offer a holistic view, encompassing individual performance and overall team productivity. Analyzing these metrics allows for a comprehensive assessment of your system’s strengths and weaknesses.
- On-Time Project Completion Rate: This metric measures the percentage of projects completed by their deadlines. A high percentage indicates efficient planning and execution.
- Task Completion Rate: This tracks the percentage of individual tasks completed successfully. A low rate may highlight issues with task assignment, prioritization, or resource allocation.
- Average Task Completion Time: This metric reveals the average time spent completing tasks. Significant deviations from the average might indicate areas needing process improvement or skill development.
- Project Budget Adherence: This measures how closely projects stay within their allocated budgets. Significant overruns point to inefficiencies in resource management or inaccurate estimations.
- Team Member Utilization: This metric assesses how effectively team members’ time is utilized. Low utilization suggests potential for improved task allocation or training.
Tracking Progress and Identifying Areas for Improvement
Tracking progress requires consistent data collection and analysis. Regularly reviewing these metrics allows for proactive adjustments to your task management processes. For example, if the “Average Task Completion Time” for a specific type of task is consistently high, it might indicate a need for additional training, improved tools, or a re-evaluation of the task’s complexity. Similarly, a low “On-Time Project Completion Rate” might signal problems with project planning or resource allocation.Consider a software development team using a Kanban board.
By tracking the time spent in each stage (e.g., backlog, in progress, testing, done), they can pinpoint bottlenecks. If tasks linger in the “testing” phase, it suggests a need for more testers or improved testing procedures. This data-driven approach allows for targeted improvements, rather than generalized adjustments.
Best Practices for Analyzing Task Management Data
Data analysis should be an iterative process. Regularly review your metrics, looking for trends and anomalies. Visualizations, such as charts and graphs, can significantly improve your understanding of the data. For instance, a line graph showing the “On-Time Project Completion Rate” over time can easily highlight periods of improvement or decline. This visual representation facilitates quick identification of areas needing attention.
Furthermore, comparing metrics across different teams or projects can reveal best practices and areas for improvement. For example, if one team consistently outperforms another, analyzing their task management processes can unveil valuable insights.
Task Management and Productivity
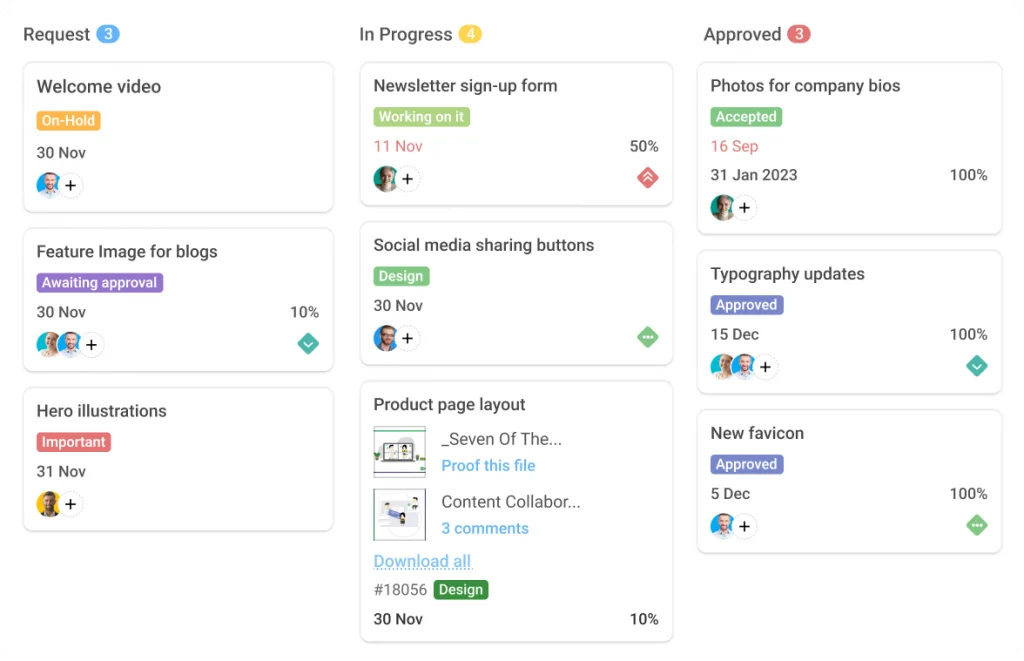
Effective task management is the cornerstone of enhanced productivity. By strategically organizing, prioritizing, and scheduling tasks, individuals and teams can streamline workflows, minimize wasted time, and achieve greater output. This isn’t just about ticking off to-do lists; it’s about creating a system that fosters focus, reduces stress, and ultimately leads to achieving more in less time.Effective task management directly correlates with increased productivity by providing structure and clarity to otherwise chaotic workloads.
Okay, so task management is key, right? I’m all about staying organized, and for me, that means leveraging the power of spreadsheets and word processing. To get started, you’ll probably want to snag a copy of Microsoft Office – you can download it here: microsoft office download. Once you’ve got that set up, creating those killer to-do lists and project timelines will be a breeze, making task management way less stressful.
A well-defined system allows for better time allocation, reducing the time spent on deciding what to do next and increasing the time spent actually doing it. This translates to more completed tasks, higher quality work, and a greater sense of accomplishment, all key components of enhanced productivity. For example, a student using a task management system to plan their study sessions and assignments might find they are able to complete their coursework more efficiently and achieve better grades, compared to a student who relies on less structured methods.
Common Pitfalls Hindering Productivity and Mitigation Strategies
Several common pitfalls frequently derail productivity. Procrastination, poor prioritization, multitasking, and a lack of clear goals all contribute to decreased efficiency. However, effective task management offers solutions to each of these challenges. Procrastination can be addressed by breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps, and scheduling specific times for tackling them. Poor prioritization is mitigated by using prioritization techniques like the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important), which helps focus on high-impact tasks first.
Multitasking, often counterproductive, is overcome by focusing on one task at a time, utilizing time-blocking techniques to dedicate uninterrupted periods to specific activities. Finally, setting clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals provides direction and purpose, preventing aimless work and enhancing overall efficiency.
Productivity Tips and Techniques Integrating with Task Management Systems
Effective task management systems are enhanced by the incorporation of various productivity tips and techniques. These strategies work best when integrated into a chosen system, allowing for seamless workflow and consistent application.
The following productivity techniques can significantly enhance the effectiveness of any task management system:
- Time Blocking: Allocate specific time slots for particular tasks. This minimizes context switching and maximizes focused work.
- Pomodoro Technique: Work in focused bursts (e.g., 25 minutes) followed by short breaks. This maintains concentration and prevents burnout.
- Eat the Frog: Tackle the most challenging or unpleasant task first thing in the morning. This builds momentum and reduces the anxiety associated with procrastination.
- Two-Minute Rule: If a task takes less than two minutes, do it immediately. This prevents small tasks from accumulating and becoming overwhelming.
- Batching Similar Tasks: Group similar tasks together (e.g., answering emails, making phone calls) to streamline workflow and reduce mental switching costs.
Adapting Task Management to Different Roles
Effective task management isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The ideal approach varies significantly depending on individual roles, responsibilities, and the specific demands of the industry. Understanding these differences is crucial for maximizing productivity and minimizing stress. This section explores how task management strategies adapt across various professional landscapes.Task management approaches differ significantly across various professional roles. Project managers, software developers, and entrepreneurs, for instance, all face unique challenges and require distinct strategies to stay organized and productive.
Similarly, industry-specific demands also influence the best task management approach.
Task Management for Project Managers
Project managers require a holistic view of numerous tasks and interdependencies. Their task management often involves detailed project plans, Gantt charts visualizing timelines and dependencies, and robust tracking mechanisms to monitor progress and identify potential roadblocks. Tools like Jira or Asana, which support collaboration and visual project tracking, are frequently used. A key focus is on meeting deadlines and managing resources effectively, requiring meticulous planning and proactive risk management.
Task Management for Software Developers
Software developers often utilize agile methodologies, breaking down projects into smaller, manageable tasks (sprints). They rely heavily on tools like Git for version control and project management platforms such as GitHub or GitLab to track bugs, features, and progress on individual tasks. Effective task management for developers prioritizes code quality, collaboration within teams, and iterative development cycles. Their approach emphasizes detailed task breakdown and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines for efficient workflow.
Task Management for Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs often juggle multiple responsibilities, from marketing and sales to product development and finance. Their task management needs to be flexible and adaptable to rapidly changing priorities. They might utilize simpler tools like to-do lists, calendar apps, or project management software tailored to their specific needs. A key aspect for entrepreneurs is prioritizing high-impact tasks that directly contribute to business growth, often requiring a dynamic approach to task prioritization based on immediate opportunities and market demands.
Their task management often reflects the ever-changing landscape of a startup.
Industry-Specific Challenges in Task Management
Different industries present unique task management challenges. For example, the healthcare industry faces stringent regulatory compliance requirements, demanding meticulous documentation and adherence to protocols. This requires task management systems that ensure audit trails and secure data handling. In contrast, the creative industries often deal with less structured tasks and require flexible task management approaches that allow for iterative development and adaptation to changing client needs.
The manufacturing sector, on the other hand, relies heavily on precise scheduling and resource allocation, necessitating robust planning and real-time tracking capabilities.
Tailoring Task Management to Individual Needs
Effective task management isn’t solely about choosing the right tools; it’s about adapting methods to personal preferences and working styles. Some individuals thrive with detailed, structured approaches, while others prefer a more flexible, less rigid system. Experimentation with different tools and techniques is crucial to find the optimal balance between structure and flexibility. For example, someone who prefers visual representations might benefit from Kanban boards, while someone who values simplicity might prefer a straightforward to-do list.
Understanding personal strengths and weaknesses is key to designing a personalized task management system that enhances productivity and reduces stress.
The Role of Technology in Task Management
Technology has fundamentally reshaped how we approach task management, moving us from simple to-do lists to sophisticated, interconnected systems. This evolution has been driven by the need for increased efficiency, better collaboration, and more insightful data analysis in managing projects and individual workloads. The integration of technology, especially emerging fields like AI and automation, promises to further revolutionize the field.The impact of emerging technologies like AI and automation on task management is profound and multifaceted.
AI-powered tools are capable of automating repetitive tasks, offering predictive analytics for scheduling and resource allocation, and providing personalized insights to improve individual and team productivity. Automation handles mundane jobs freeing up human workers to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their work. However, the successful integration of these technologies requires careful planning and consideration of potential challenges.
Impact of AI and Automation on Task Management
AI’s influence on task management manifests in several key areas. Predictive scheduling algorithms, for example, can analyze historical data and project timelines to forecast potential bottlenecks and suggest optimized schedules. AI-powered assistants can automatically prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance, reducing the cognitive load on users. Furthermore, AI can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and trends in task completion, helping managers optimize workflows and improve overall team performance.
Automation plays a vital role in this process by streamlining repetitive tasks such as data entry, email management, and meeting scheduling.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Integrating AI into Task Management Workflows
The benefits of integrating AI are significant, including increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and enhanced decision-making. By automating routine tasks, AI frees up human resources for more complex and creative work. The improved accuracy offered by AI algorithms reduces errors and ensures that tasks are completed correctly and on time. Furthermore, AI-powered analytics provide valuable insights that enable better decision-making, leading to more effective task management strategies.
However, the integration of AI also presents challenges. The initial investment in AI-powered tools can be substantial, and there’s a need for specialized expertise to implement and maintain these systems. Concerns around data privacy and security also need careful consideration. Finally, over-reliance on AI can lead to a lack of human oversight and potentially hinder creativity and critical thinking.
Hypothetical Scenario: AI-Powered Task Management
Imagine a marketing team using an AI-powered task management platform. The platform analyzes each team member’s past performance, current workload, and project deadlines. It then automatically assigns tasks based on individual skills and availability, optimizing resource allocation. If a project is falling behind schedule, the AI system identifies potential bottlenecks and suggests alternative solutions, such as reassigning tasks or adjusting deadlines.
The platform also analyzes email communication and meeting notes to automatically update task statuses and flag potential conflicts. In this scenario, the AI acts as an intelligent assistant, handling routine tasks and providing valuable insights, allowing the team to focus on strategic planning and creative execution. The system learns and adapts over time, becoming more effective at managing the team’s workload and achieving project goals.
This AI-driven approach enhances collaboration and communication, ultimately improving project outcomes and team productivity.
Overcoming Procrastination and Maintaining Momentum

Procrastination is a common enemy of productivity, hindering task completion and causing unnecessary stress. Understanding its root causes and employing effective strategies to overcome it is crucial for achieving goals and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. This section explores common procrastination triggers and offers practical techniques to regain control and stay on track.Procrastination stems from various sources, often intertwined and specific to the individual.
Fear of failure, perfectionism, feeling overwhelmed by a task’s complexity, poor time management skills, and a lack of clear goals all contribute to delaying or avoiding work. Understanding these underlying issues is the first step towards developing effective countermeasures.
Common Causes of Procrastination and Strategies for Overcoming Them
Several factors contribute to procrastination. Fear of failure can paralyze individuals, preventing them from even starting a task. Perfectionism, while seemingly positive, often leads to excessive self-criticism and endless revisions, delaying completion. Feeling overwhelmed by a large task can be daunting, leading to avoidance. Poor time management, such as a lack of planning or unrealistic scheduling, also contributes significantly.
Finally, a lack of clear goals or understanding of the task’s purpose can make it feel meaningless and unmotivating. To combat these, break down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. This makes the overall project less intimidating and provides a sense of accomplishment as each smaller task is completed. Setting realistic deadlines and utilizing time management techniques like the Pomodoro Technique (working in focused bursts with short breaks) can also improve focus and efficiency.
Practicing self-compassion and reframing negative self-talk are essential for building confidence and reducing the fear of failure.
Techniques for Staying Motivated and Maintaining Momentum in Task Completion
Maintaining momentum requires consistent effort and strategic planning. Rewarding yourself after completing milestones, no matter how small, reinforces positive behavior and provides motivation. Publicly committing to goals, such as sharing them with a friend or colleague, adds an element of accountability. Visualizing success and focusing on the positive outcomes of completing the task can also boost motivation.
Regularly reviewing progress and adjusting plans as needed helps to stay on track and prevent feelings of being overwhelmed. Finding an accountability partner or joining a study group can provide support and encouragement. Furthermore, prioritizing self-care, including sufficient sleep, exercise, and healthy eating, is essential for maintaining energy levels and focus. A well-rested and healthy individual is better equipped to tackle challenges and stay motivated.
Addressing Procrastination Within a Specific Task Management System
Integrating strategies to combat procrastination directly into a task management system enhances their effectiveness. For example, within a Kanban system, you might create a “Procrastination Pile” column. Tasks moved here are reviewed for underlying causes (fear, overwhelm, etc.) and broken down into smaller, actionable steps. Then, they are re-assigned to the “In Progress” column with realistic deadlines. In a calendar-based system, schedule specific times for tackling challenging tasks, treating them like important appointments.
Set reminders and allocate sufficient time to avoid feeling rushed. Utilize the system’s features, such as progress tracking and notifications, to monitor your work and celebrate achievements. Regularly review your task list and adjust priorities as needed. By actively incorporating anti-procrastination techniques into your chosen system, you create a proactive and supportive environment for consistent task completion.
Personal Task Management vs. Project Management
Personal task management and project management, while both focused on getting things done, differ significantly in scope, complexity, and approach. Understanding these differences is crucial for maximizing efficiency and productivity, whether you’re tackling your personal to-do list or leading a complex team project.Personal task management focuses on individual goals and responsibilities. It’s about organizing and prioritizing tasks to achieve personal objectives, often within a less structured framework.
Project management, on the other hand, involves planning, executing, monitoring, and closing a specific project with defined deliverables, timelines, and resources. It’s inherently more complex and collaborative.
Scope and Complexity Differences
Personal task management typically involves a smaller scope of work. The tasks are usually less interconnected and have a shorter time horizon. Think grocery shopping, paying bills, or scheduling appointments. Project management, however, deals with larger, more complex undertakings. These projects often involve multiple interdependent tasks, a larger team, and a longer timeline.
Examples include launching a new product, building a house, or planning a large-scale event. The complexity increases exponentially with the number of stakeholders and the intricacy of the project’s phases.
Tools and Technologies
The tools used for personal task management are often simpler and less sophisticated. Many individuals rely on to-do lists, calendars, or basic note-taking apps. Project management, however, frequently utilizes more advanced software and tools like project management platforms (Asana, Trello, Jira), collaboration software (Slack, Microsoft Teams), and Gantt charts for visualizing project timelines and dependencies. The choice of tools directly reflects the scale and complexity of the undertaking.
Situational Appropriateness
Personal task management is best suited for individual goals and routine tasks. If you’re aiming to improve your personal organization, streamline your daily routine, or achieve individual goals, a personal task management approach is ideal. Project management, conversely, is most appropriate for complex endeavors involving multiple people, resources, and clearly defined objectives and deliverables. A large-scale construction project or the development of a new software application are perfect examples where a structured project management approach is essential for success.
The key distinction lies in the scale and collaborative nature of the work.
The Future of Task Management
The landscape of task management is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting work dynamics. We’re moving beyond simple to-do lists and into a world of sophisticated systems designed to enhance productivity and collaboration. This evolution presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges for individuals and organizations alike.The next five to ten years will likely witness a significant transformation in how we approach task management, driven by several key factors.
Increased automation, improved AI integration, and a greater focus on user experience will redefine the field.
AI-Powered Task Management
Artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize task management. We can expect to see AI-powered systems that not only organize tasks but also predict priorities, suggest optimal schedules, and even proactively identify and mitigate potential roadblocks. Imagine a system that learns your work patterns, anticipates your needs, and automatically adjusts your schedule based on incoming emails, calendar events, and project deadlines.
This level of automation could significantly reduce cognitive load and free up time for more strategic work. For example, an AI could analyze a project’s timeline and resource allocation, flagging potential delays before they become critical issues. This predictive capability would allow for proactive adjustments and prevent costly overruns.
Hyper-Personalization and User Experience
Future task management tools will be highly personalized, adapting to individual work styles and preferences. We’ll see systems that learn from user behavior, offering customized suggestions and interfaces. The focus will shift from generic task lists to personalized dashboards that provide at-a-glance insights into progress, priorities, and potential bottlenecks. Imagine a system that automatically categorizes tasks based on your past behavior, using natural language processing to understand the context and urgency of each item.
This level of personalization would significantly improve efficiency and user satisfaction.
Enhanced Collaboration and Integration
Task management tools will become even more integrated with other productivity applications. Seamless integration with communication platforms, calendar apps, and project management software will create a unified workflow, minimizing context switching and improving team collaboration. For instance, a task management system might directly integrate with a video conferencing tool, allowing for quick team check-ins and real-time updates on task progress.
This level of integration would streamline workflows and enhance communication, resulting in improved project outcomes.
The Challenge of Data Security and Privacy
As task management systems become increasingly sophisticated and data-driven, concerns about data security and user privacy will become paramount. Robust security measures will be crucial to protect sensitive information and maintain user trust. This will require a multi-faceted approach, including advanced encryption techniques, strict access controls, and transparent data usage policies. Organizations will need to invest in robust security infrastructure and implement best practices to mitigate the risks associated with storing and processing sensitive data.
The potential for data breaches and misuse of personal information presents a significant challenge that must be addressed proactively.
The Opportunity for Increased Productivity and Efficiency
The advancements in task management technology offer a significant opportunity to boost overall productivity and efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, providing intelligent insights, and facilitating seamless collaboration, these systems can empower individuals and teams to achieve more in less time. This increased efficiency could translate to significant cost savings for organizations and improved work-life balance for individuals. The potential for increased productivity is immense, provided that the challenges related to data security, user adoption, and ethical considerations are effectively addressed.
Outcome Summary: Task Management
So, there you have it – a whirlwind tour through the world of task management! From choosing the perfect app to conquering procrastination, mastering effective task management isn’t just about checking things off a list; it’s about building a system that works for
-you*, boosting your productivity, and ultimately, achieving your goals with less stress and more satisfaction. Now go forth and conquer your to-do list!
Essential Questionnaire
What’s the difference between task management and project management?
Task management focuses on individual tasks and their completion, while project management involves planning, executing, and closing larger, more complex projects with multiple tasks and deadlines.
How do I choose the right task management tool?
Consider your needs and preferences. Do you prefer a simple to-do list, or something more collaborative? Free vs. paid options? Try out a few free trials before committing.
What if I’m overwhelmed by my tasks?
Break down large tasks into smaller, more manageable chunks. Prioritize ruthlessly, focusing on the most important and urgent items first. Don’t be afraid to delegate or ask for help!
How can I prevent burnout?
Set realistic goals, take regular breaks, and prioritize self-care. Don’t be afraid to say no to additional tasks if you’re already feeling overwhelmed. Remember, sustainable productivity is key.
What are some good resources for learning more about task management?
Check out online courses, productivity blogs, and books on time management and task management techniques. Many free resources are available online!


